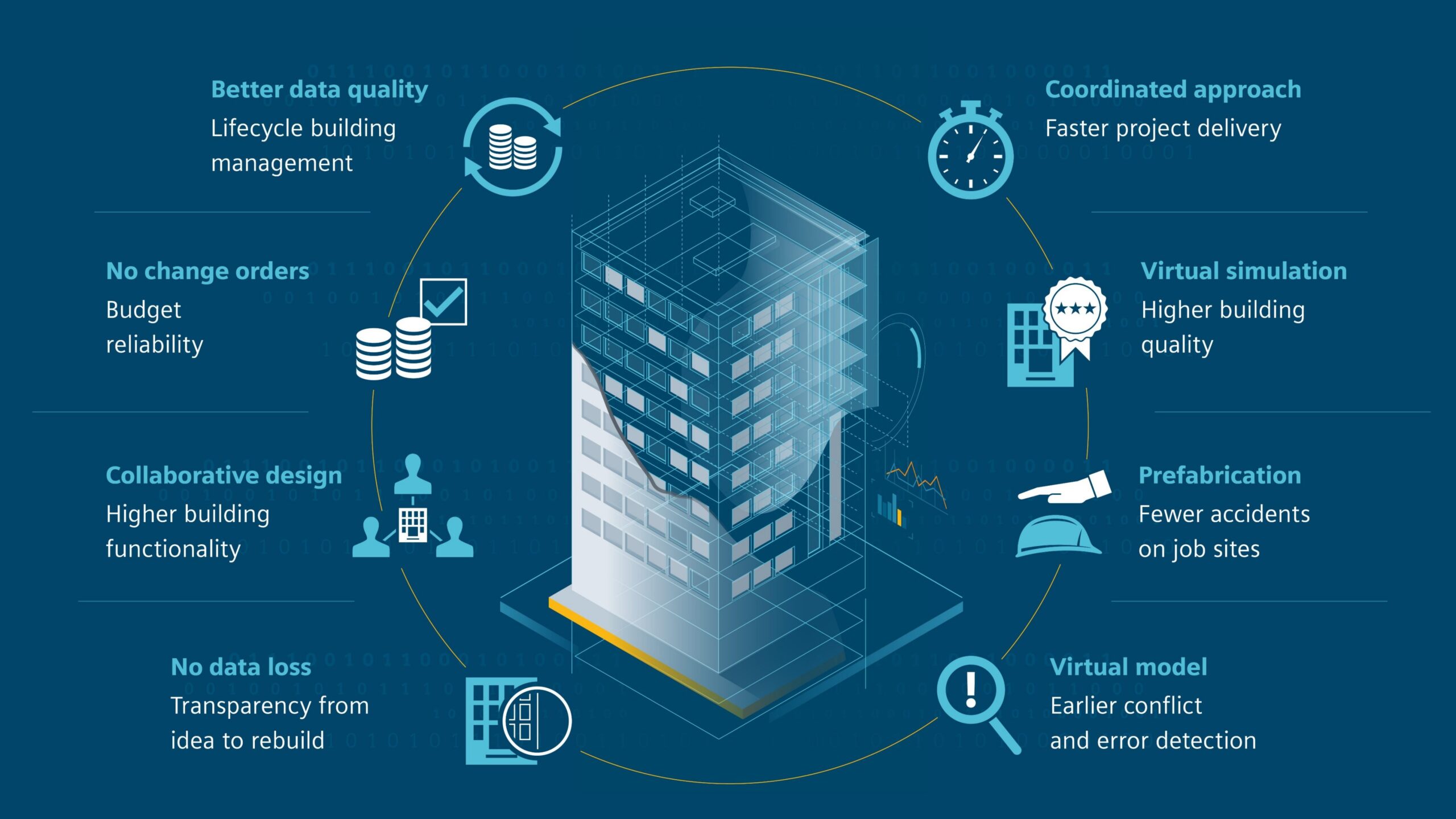
Building Information Modeling (BIM) Building Information Modeling (BIM) serves as a transformative approach, offering a digital representation of a facility's physical and functional characteristics. By embracing this technology-driven process, professionals can create and manage detailed digital models throughout the entire lifecycle of a project—from initial design and construction through to ongoing operation and maintenance. Key Elements of BIM At the heart of BIM lies 3D Modeling, which enables the creation of intricate models that encompass geometry, spatial relationships, and vital geographic information. Additionally, Data Management is central to BIM, integrating various project data—such as materials, specifications, and quantities—into a comprehensive information hub. One of the standout features of BIM is its ability to enhance Collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and clients. This improved communication significantly reduces conflicts and streamlines the decision-making process. Moreover, BIM is invaluable for Lifecycle Management, supporting every stage of a project and facilitating seamless transitions over time. The Power of Visualization The advanced visualization capabilities within BIM allow stakeholders to see realistic representations of projects, making it easier to navigate design decisions and convey concepts effectively. This visualization not only aids in clarity but also enhances stakeholder engagement. Advantages of Implementing BIM The benefits of adopting BIM are multifaceted. Notably, it leads to Improved Accuracy, dramatically reducing errors and omissions through precise modeling and simulations. This precision fosters Efficiency, streamlining workflows and enhancing productivity thanks to better collaboration and information sharing among team members. Additionally, BIM can result in substantial Cost Savings by identifying potential issues early in the design phase, thereby minimizing rework costs and helping to manage budgets effectively. Moreover, BIM plays a crucial role in promoting Sustainability by enabling analysis and optimization of building performance in terms of energy efficiency and resource management. Diverse Applications of BIM The versatility of BIM is evident across various sectors: · In Architecture, it helps design building layouts, systems, and aesthetics. · For Structural Engineering, BIM models structural components and analyzes load-bearing capacities. · Within MEP Engineering, it supports the planning and coordination of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems. · Construction Management benefits from BIM by optimizing scheduling, logistics, and overall project management. · Finally, in Facility Management, BIM assists in overseeing maintenance, renovations, and effective space utilization after construction.
Popular BIM Software Several software options have risen to prominence in the BIM landscape. Autodesk Revit is widely favored for architectural design and engineering applications, while Archicad stands out for its user-friendly interface geared towards architects. Navisworks is invaluable for project review and clash detection, and Tekla Structures focuses on structural modeling and detailing. By incorporating BIM into their workflows, organizations within the construction and architecture industries can unlock significant improvements in project outcomes and operational efficiency throughout the building's lifecycle. Embracing this innovative approach is not just beneficial—it's becoming essential in today’s competitive landscape.